

The higher the ISO value, the more sensitive the sensor is to light, the less light is needed to properly expose an image, and the more of a chance of digital noise occurring.ĭigital noise is specks of color and light in an image (usually in areas of shadow and solid color) that reduce the image’s detail and quality. The lower the ISO value, the less sensitive the sensor is to light, the more light is needed to properly expose an image, and the less of a chance of digital noise occurring. ISO determines how sensitive your camera’s sensor is to light. What do the f stop numbers mean F-stop (aka f-number) is the number that you see on your camera or lens as you adjust the size of your aperture. This will vary for different types of situations. The aperture regulates light by varying the size of the hole through which the light passes, and ISO regulates how sensitive to the light the sensor (or film) is. Generally, you’ll need to use a tripod or steady the camera in some other way for shutter speeds that are slower than 1/125th or 1/200th of a second to avoid blurring. Shutter speeds vary from many thousandths of a second to several hours. The shorter amount of time that the shutter is open, the less light reaches the sensor for a given f-stop value. The longer amount of time that the shutter is open, the more light reaches the sensor for a given f-stop value. The shutter is like a curtain that blocks the camera’s sensor from light until it is opened to take a picture. Shutter speed determines the length of time that the shutter is open and exposes the camera’s sensor to light. One thing that people often find confusing is that the larger the f/. You may need to adjust the shutter speed to be faster or slower or adjust the ISO to be higher or lower. Aperture is measured in f-stops, often referred to as f/number, e.g. The aperture works with other settings (shutter speed, ISO, etc.) to achieve proper exposure. You need to take into consideration how much available light is in the scene (if only using natural light) and how deep or shallow you want the depth of field to be. These f-stop values are good for macro shots or other scenes in which you want a specific area to be in focus with things in the foreground or background to be out of focus. A larger aperture has a shallower depth of field. These f-stop values are good for landscape shots or other scenes in which you want things in the foreground and the background to be in focus.

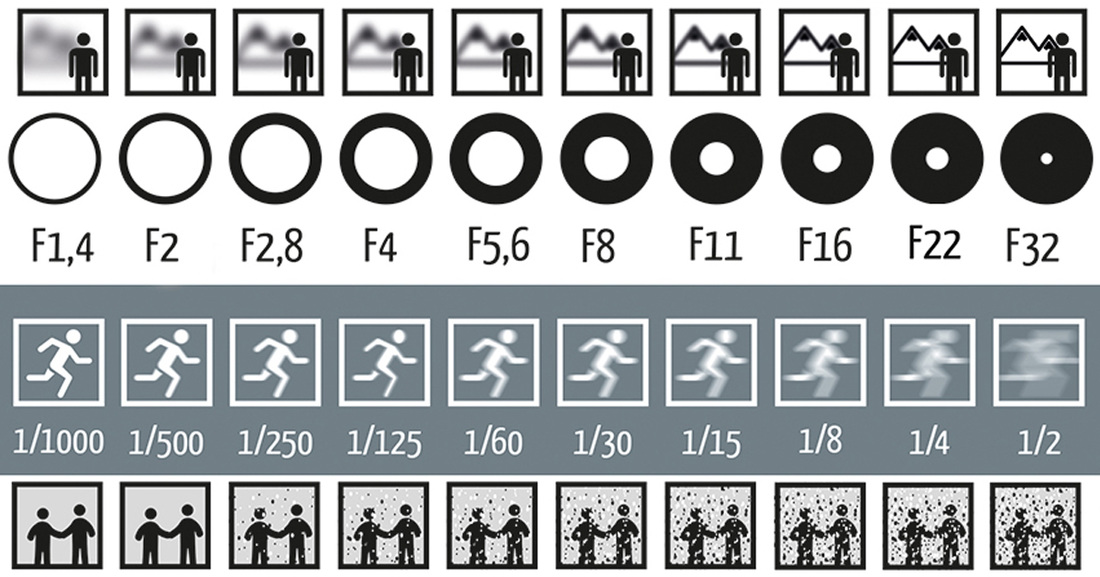
A smaller aperture has a deeper depth of field. The f-stop value also determines the depth of field. f/1.4), the larger the aperture and the more light is exposed to the sensor for a given amount of time. f/22), the smaller the aperture and the less light is exposed to the sensor for a given amount of time. The aperture is the hole through which light enters the camera through the lens and is exposed to the sensor. An f-stop is the measurement of the opening of the aperture.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
